The Ultimate Guide to Optimising for Core Web Vitals

In today’s digital landscape, user experience (UX) is crucial for online success. Google’s Core Web Vitals are at the heart of this focus, providing essential metrics that measure and enhance a website’s loading speed, responsiveness, and visual stability. Core Web Vitals impact not only user satisfaction but also search engine ranking, making them crucial for businesses, developers, and site owners.
What Are Core Web Vitals?

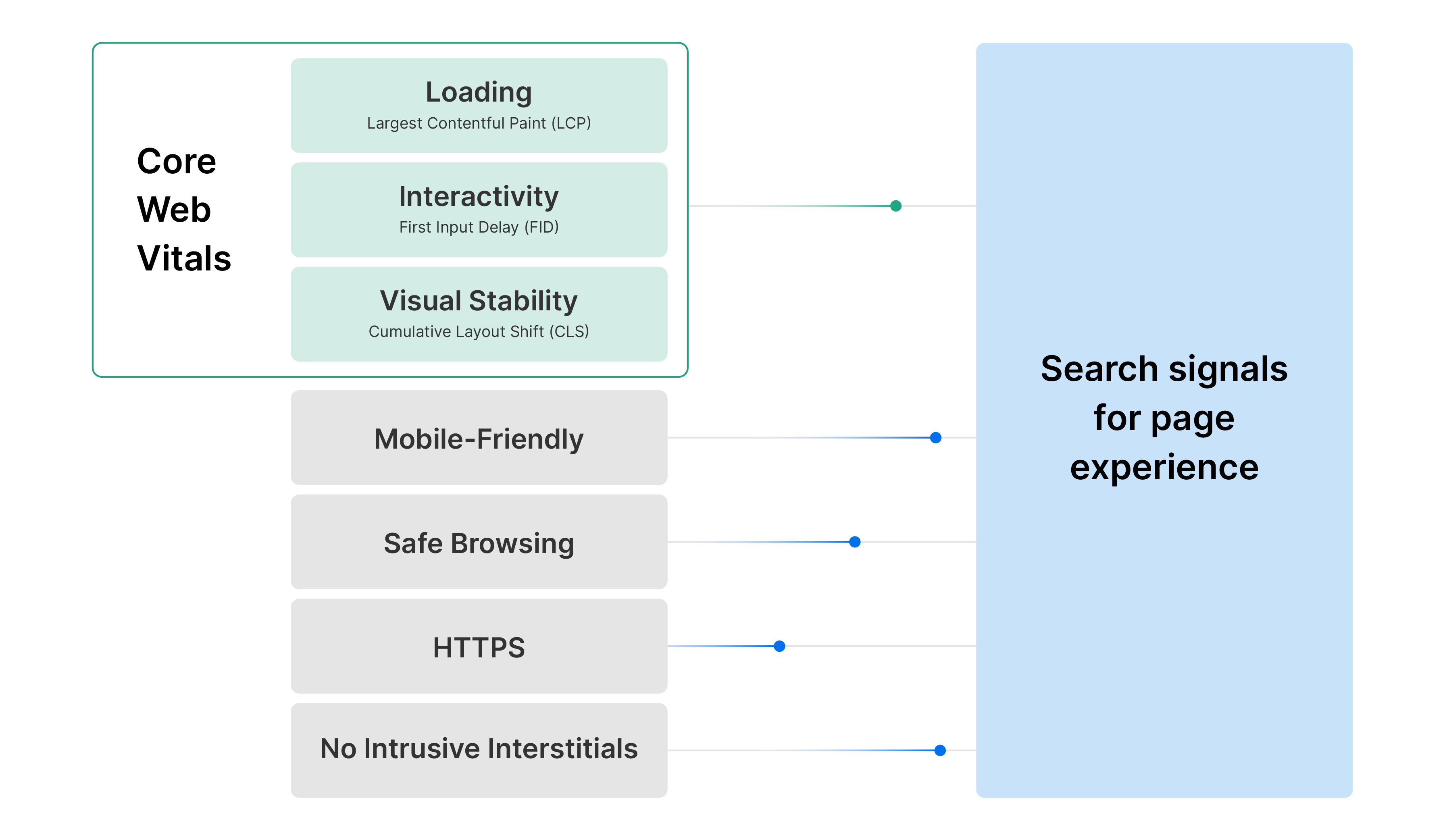
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics designed by Google to assess a site’s user experience through three primary areas: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These metrics analyze how quickly a site loads, responds, and maintains visual stability.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures loading time for the largest visible element on a page, aiming for 2.5 seconds or faster for a smooth user experience.
- First Input Delay (FID) tracks how quickly the site responds to a user’s initial interaction, with an ideal FID under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures visual stability to prevent unexpected content shifts, with a score below 0.1 indicating minimal disruption to the user.
Each of these metrics provides insights into areas that can enhance user experience and engagement, making Core Web Vitals essential for improving site performance.
What Is Core Web Vitals in Google Search Console?
Core Web Vitals in Google Search Console refers to a set of reports that help website owners and webmasters understand how well their pages perform in terms of the user experience metrics defined by Core Web Vitals. These reports specifically focus on the three key metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Here’s how it works:
- Overview Report: The Core Web Vitals report provides an overview of the performance of your pages across different devices (desktop and mobile). It categorizes pages as “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor” based on the performance thresholds for each metric.
- Detailed Metrics: Each metric is displayed along with the percentage of URLs that meet the recommended thresholds. You can see how many of your pages are performing well and which ones need attention.
- Page List: The report provides a list of individual pages that fall into each performance category, allowing you to identify specific URLs that may need optimization.
- Improvement Suggestions: Google Search Console may also offer suggestions for improvements, pointing out specific issues that could be impacting performance, such as image sizes or JavaScript execution time.
- Tracking Over Time: The Core Web Vitals report allows you to track performance over time, helping you see how changes you make affect user experience.
By monitoring Core Web Vitals in Google Search Console, webmasters can gain insights into how their sites perform in real-world conditions and make informed decisions to enhance user experience and potentially improve search rankings.
Why Are Core Web Vitals Important for Websites?
Core Web Vitals are essential for websites for several key reasons, primarily revolving around user experience, SEO performance, and overall site effectiveness. Here are some of the main reasons why these metrics matter:
1. Enhancing User Experience
Core Web Vitals directly measure aspects of user experience that significantly affect how visitors interact with a website. Metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) focus on the loading speed, responsiveness, and visual stability of a site.
- LCP ensures that the main content loads quickly, allowing users to see what they came for without unnecessary delays.
- FID measures the responsiveness of a site, ensuring that users can interact with elements (like buttons and links) immediately after they load.
- CLS assesses how stable the visual elements are, preventing frustrating shifts that can cause users to click on the wrong items.
A site that performs well in these areas provides a smoother, more enjoyable experience, which is critical for retaining visitors.
2. Impacting SEO and Search Rankings
Google has integrated Core Web Vitals into its ranking algorithms, making them a significant factor in search engine optimization (SEO). Sites that score well on these metrics are more likely to rank higher in search results.
- According to studies, websites that optimize their Core Web Vitals can improve their positions in search rankings, leading to increased visibility and organic traffic.
- A well-performing site not only attracts more visitors but also keeps them engaged, reducing bounce rates and increasing the likelihood of conversions.
For instance, research indicates that a 1-second improvement in page load time can lead to a 7% increase in conversions, underscoring how vital these metrics are for both user engagement and SEO.
3. Reducing Bounce Rates
As mentioned earlier, loading times have a direct correlation with bounce rates. If a website takes too long to load, users are more likely to leave and seek faster alternatives.
- Studies reveal that as loading time increases from 1 to 3 seconds, the probability of bounce rises by 32%. At 5 seconds, this number escalates to 90%.
- By improving Core Web Vitals, websites can significantly decrease bounce rates, leading to a higher likelihood of retaining users and converting them into customers.
4. Increasing Conversion Rates
Websites that prioritize Core Web Vitals are better positioned to convert visitors into customers. Fast-loading, responsive, and visually stable sites create an environment where users feel comfortable making purchases or engaging with content.
- Optimizing these metrics can lead to improved conversion rates, as users are less likely to abandon their carts or exit the site during the purchasing process.
- Businesses can see a tangible return on investment (ROI) when focusing on Core Web Vitals, as a positive user experience is closely linked to revenue growth.
5. Encouraging Mobile Responsiveness
With the rise of mobile browsing, optimizing Core Web Vitals also encourages better mobile responsiveness. Google’s emphasis on mobile-first indexing means that sites need to perform well on mobile devices.
- Core Web Vitals promote practices that enhance performance across all devices, ensuring that users have a seamless experience regardless of how they access the site.
- A site that loads quickly and maintains stability on mobile can capture a broader audience, further driving traffic and engagement.
6. Aligning with Google’s Priorities
As Google continuously evolves its algorithms to focus more on user experience, aligning your website with these priorities through Core Web Vitals optimization becomes essential. By staying updated with the latest metrics and best practices, site owners can ensure they meet the search engine’s expectations, ultimately improving their online presence.
Does Core Web Vitals Affect SEO and Rankings?
Yes, Core Web Vitals significantly affect SEO and rankings. Google has made it clear that user experience is a critical factor in its ranking algorithms, and Core Web Vitals are a key component of that experience. Here’s how they influence SEO and rankings:
- Ranking Factor: Since June 2021, Google has officially included Core Web Vitals in its ranking criteria as part of the “Page Experience” update. Websites that perform well on these metrics are more likely to rank higher in search results, especially in competitive niches.
- User Engagement: Pages that load quickly, are interactive, and stable during loading encourage users to stay longer. Higher engagement rates can lead to lower bounce rates, which are signals to Google that a site is providing value, potentially boosting its ranking.
- Mobile-First Indexing: With Google prioritizing mobile versions of websites for indexing and ranking, optimizing for Core Web Vitals helps ensure a good experience on mobile devices. As more users access the web via mobile, this becomes increasingly important for SEO.
- Impact on Click-Through Rates (CTR): Higher rankings generally lead to increased visibility and traffic. However, if a page performs poorly on Core Web Vitals, even if it ranks well, users may still choose to click on other results that provide a better experience. This can indirectly affect the site’s rankings over time.
- Site Credibility and Trust: Websites that load quickly and provide a seamless user experience can build credibility and trust with users. A good reputation can lead to more backlinks, social shares, and overall authority, which are also positive signals for SEO.
- Technical SEO Improvements: Optimizing for Core Web Vitals often involves addressing underlying technical issues on a website. Improved site performance can positively impact crawlability and indexability, further enhancing SEO.
- Regular Monitoring: Since Core Web Vitals are part of ongoing assessments of user experience, regular monitoring and optimization can help maintain or improve rankings over time, keeping the site competitive.
In, Core Web Vitals are not the only factors influencing SEO and rankings, they play a crucial role in providing a positive user experience that can lead to better performance in search engine results. Prioritizing these metrics can significantly benefit a website’s visibility and success online.
You May Also Like to Read: A Comprehensive Guide to Keyword Research and On-Page SEO For Ranking on Google
When Did Core Web Vitals Start and How Have They Evolved?
Core Web Vitals were launched by Google in May 2020 as part of its ongoing commitment to improving UX across the web. Over time, Google has refined and updated these metrics, making it essential for site owners to stay current with Core Web Vitals monitoring and optimization practices. Google releases regular updates to ensure these metrics align with real-world user expectations, emphasizing the need for continuous Core Web Vitals audits and adjustments.
Core Web Vitals are fundamental metrics that enable site owners to assess and enhance user experience on their sites. By focusing on LCP, FID, and CLS, businesses can optimize Core Web Vitals to ensure better rankings and improved user engagement, making Core Web Vitals optimization services a valuable asset for any website. Embracing these metrics not only enhances SEO potential but also drives higher conversions, making it an essential investment for long-term online success.
Why Are Core Web Vitals Essential for SEO?
Core Web Vitals are essential for SEO for several key reasons:
- Direct Ranking Factors: Google has incorporated Core Web Vitals as direct search ranking signals in its search algorithm. This means that a website’s performance on these metrics can directly influence its position in search results.
- User Experience: Core Web Vitals focus on important aspects of user experience, such as loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. A positive user experience leads to higher engagement, lower bounce rates, and increased time spent on the site—all factors that can improve SEO.
- Mobile Optimization: As mobile-first indexing becomes the norm, optimizing for Core Web Vitals ensures that websites perform well on mobile devices. Given that more users browse the web on smartphones, this optimization is crucial for maintaining visibility in search results.
- Competitive Advantage: In competitive markets, optimizing for Core Web Vitals can give websites an edge over competitors. A site that loads faster and provides a better user experience is more likely to attract and retain visitors, leading to higher search rankings.
- Reduced Load Times: Faster loading times directly improve user satisfaction and engagement. Users are less likely to abandon a site that loads quickly, which can lower bounce rates and positively influence SEO performance.
- Increased Conversions: Good performance on Core Web Vitals can lead to higher conversion rates. Websites that provide a smooth experience are more likely to convert visitors into customers, which can indirectly enhance SEO by improving user engagement signals.
- Impact on Click-Through Rates (CTR): Higher rankings can lead to more visibility, but if users click on a result and find a poor experience, they may quickly return to search results. This can negatively impact CTR and, subsequently, rankings. A site that performs well on Core Web Vitals is more likely to retain visitors.
- Long-Term Strategy: Focusing on Core Web Vitals aligns with a long-term SEO strategy. As Google continues to prioritize user experience, optimizing for these metrics ensures that websites remain compliant with evolving search engine standards.
- Technical SEO Benefits: Improving Core Web Vitals often requires addressing technical aspects of a website, such as image optimization and script loading times. These improvements can enhance overall site performance and indexability, benefiting SEO efforts.
In, Core Web Vitals are essential for SEO because they directly affect how search engines assess the quality of a site, influence user engagement, and ultimately determine a site’s visibility in search results. Prioritizing these metrics can lead to better rankings, increased traffic, and improved overall performance.
Are Core Web Vitals a Ranking Factor?
–
Yes, Core Web Vitals are indeed a ranking factor in Google’s search algorithm. Introduced as part of Google’s ongoing efforts to improve user experience across the web, Core Web Vitals became officially integrated into the ranking criteria in June 2021. Here’s a detailed look at why and how Core Web Vitals influence search rankings:
1. Google’s Focus on User Experience
Google has always prioritized user experience, and the introduction of Core Web Vitals underscores this commitment. The metrics—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—are designed to measure specific aspects of user interaction with web pages. By focusing on these metrics, Google aims to ensure that users have fast, responsive, and visually stable experiences on the sites they visit.
2. Direct Correlation with User Behavior
Research has shown that user behavior is closely tied to page performance metrics. For instance:
- Sites with a good LCP score (2.5 seconds or less) tend to keep users engaged and reduce bounce rates, as visitors are more likely to stay on a site that loads quickly.
- A FID score of under 100 milliseconds ensures that users can interact with page elements without delay, enhancing the overall experience.
- Maintaining a low CLS score (below 0.1) prevents frustrating layout shifts, which can lead to accidental clicks and user frustration.
These behaviors directly influence a site’s performance in search rankings, as Google’s algorithm takes user engagement metrics into account.
3. Implications for SEO Strategies
Since Core Web Vitals are now a ranking factor, they must be included in any effective SEO strategy. Websites that do not meet Google’s thresholds for these metrics may experience a drop in rankings. This is particularly true for competitive niches where user experience is critical. Consequently, businesses that prioritize optimizing Core Web Vitals can gain a significant advantage over their competitors who neglect these metrics.
4. Visibility and Traffic Impact
The ranking factor status of Core Web Vitals can lead to increased visibility and organic traffic. A higher ranking in search results typically translates to more clicks and visits, which can enhance brand awareness and ultimately drive sales. Conversely, sites that fail to optimize for Core Web Vitals risk losing ground in search results, leading to reduced traffic and missed opportunities.
5. Mobile-First Indexing
As part of its emphasis on mobile usability, Google has moved to a mobile-first indexing approach. This means that the mobile version of a site is primarily used for indexing and ranking. Since Core Web Vitals apply to both desktop and mobile experiences, optimizing for these metrics is crucial for maintaining high rankings across devices. A site that performs well on mobile, including good scores on Core Web Vitals, is more likely to rank favorably in search results.
6. Continuous Updates and Adaptation
Google is known for continuously updating its algorithms to better align with user expectations. Core Web Vitals are likely to evolve as web standards and user behavior change over time. Therefore, website owners need to stay informed about these updates and continuously monitor their Core Web Vitals to maintain and improve their search rankings.
Core Web Vitals are a significant ranking factor within Google’s search algorithm. By emphasizing user experience through metrics that measure loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, Google encourages webmasters to create high-performing sites that cater to user needs. Websites that optimize their Core Web Vitals can improve their rankings, drive more traffic, and ultimately enhance user engagement and conversions. For businesses aiming for online success, prioritizing Core Web Vitals is no longer optional but essential.
Does Core Web Vitals Affect Rankings on Google?
Yes, Core Web Vitals do affect rankings on Google. Since their introduction as part of Google’s ranking criteria in June 2021, Core Web Vitals have become a vital component of search engine optimization (SEO). Here’s an in-depth look at how these metrics influence search rankings:
1. User Experience as a Ranking Criterion
Google’s primary goal is to provide users with the most relevant and satisfying search results. To achieve this, Google has integrated Core Web Vitals—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—into its ranking algorithm to measure specific aspects of user experience. By assessing these metrics, Google ensures that websites offering fast load times, smooth interactivity, and stable layouts are rewarded with higher rankings.
2. Impact of Loading Speed
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures how quickly the largest visible element on a webpage loads. An ideal LCP score is 2.5 seconds or less. Pages that load quickly are less likely to see high bounce rates, meaning users are more likely to stay and engage with the content.
- Research indicates that when a website’s loading time increases from 1 to 3 seconds, the probability of a bounce increases by 32%. If loading time reaches 5 seconds, the bounce probability jumps to 90%. Therefore, sites with good LCP scores are more likely to retain users and maintain a favorable ranking.
3. Influence of Interactivity
- First Input Delay (FID) measures the time it takes for a site to respond to a user’s first interaction. An FID score of less than 100 milliseconds is ideal. Sites that respond quickly to user inputs enhance engagement and satisfaction.
- When users experience delays, they are more likely to abandon the site. As Google considers user engagement signals as part of its ranking criteria, sites that provide a faster, more responsive experience can see an improvement in their search rankings.
4. Visual Stability Matters
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) assesses how stable the visual layout of a webpage is during loading. A score of less than 0.1 indicates minimal layout shifts. Sudden shifts in content can frustrate users, leading to accidental clicks and a poor overall experience.
- By maintaining low CLS scores, websites can ensure users are not disturbed by unexpected changes, enhancing the user experience and positively impacting rankings.
5. The Role of Mobile Responsiveness
Google employs a mobile-first indexing approach, meaning that the mobile version of a site is primarily used for indexing and ranking. Since Core Web Vitals apply to both desktop and mobile versions, optimizing these metrics is crucial for maintaining high rankings across devices. Websites that perform well on mobile—ensuring quick loading times and stable layouts—are more likely to rank favorably in search results.
6. Competitive Advantage
With Core Web Vitals now influencing rankings, websites that prioritize optimization for these metrics can gain a competitive edge. A site that excels in Core Web Vitals is more likely to outrank competitors that do not focus on these metrics. This is particularly important in competitive niches, where user experience can be a key differentiator.
7. Ongoing Adaptation and Monitoring
Google regularly updates its algorithms to enhance user experience and adapt to changing web standards. As such, website owners must stay informed about any changes related to Core Web Vitals. Continuous monitoring and optimization of these metrics can help maintain and improve search rankings over time.
Core Web Vitals significantly affect rankings on Google. By measuring key aspects of user experience—loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability—Google ensures that users receive high-quality results. Websites that optimize their Core Web Vitals can improve their rankings, attract more traffic, and enhance user engagement. For businesses aiming for success in the digital landscape, focusing on Core Web Vitals is essential for achieving strong search rankings and ensuring a satisfying user experience.
Is Technical SEO Part of Core Web Vitals?

Yes, technical SEO is an integral part of optimizing for Core Web Vitals. While Core Web Vitals specifically focus on user experience metrics such as loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, achieving optimal scores in these areas often requires a strong technical foundation. Here’s how technical SEO relates to Core Web Vitals:
1. Understanding Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals consist of three main metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance, specifically the time it takes for the largest content element (like an image or text block) to become visible within the viewport. An ideal LCP score is 2.5 seconds or less.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity by assessing how long it takes for a user’s first interaction (like clicking a button) to be processed. A good FID score is less than 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability, quantifying how much content shifts during the loading process. A CLS score of less than 0.1 indicates a stable layout.
These metrics are crucial for enhancing user experience, and addressing them often involves technical SEO practices.
2. Optimizing for Loading Speed (LCP)
Technical SEO plays a significant role in improving LCP scores. Here are some key practices:
- Minimizing Server Response Times: Using a reliable hosting provider and optimizing server configurations can significantly reduce loading times. This is a core aspect of technical SEO.
- Implementing Caching: Effective caching strategies, such as browser caching and server-side caching, can help serve pages faster to returning users.
- Image Optimization: Compressing images and using appropriate formats (like WebP) can significantly enhance loading speed, improving LCP scores.
- Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN): CDNs distribute content across various geographic locations, enabling quicker access to resources for users, thus improving loading times.
3. Enhancing Interactivity (FID)
Improving FID scores also requires a focus on technical SEO:
- Optimizing JavaScript Execution: Heavy JavaScript files can delay the response to user interactions. Minimizing, deferring, or asynchronously loading JavaScript can improve FID scores.
- Reducing Main Thread Blocking Time: Ensuring that critical tasks are completed quickly and efficiently can enhance user interactivity, contributing to a better FID score.
4. Maintaining Visual Stability (CLS)
CLS is closely linked to technical SEO as well:
- Avoiding Layout Shifts: Ensuring that images have specified dimensions and avoiding the use of dynamic ads can prevent unexpected shifts in content, resulting in a lower CLS score.
- Using CSS for Layouts: Proper use of CSS and positioning techniques can help maintain a consistent layout, reducing visual shifts as content loads.
5. Mobile Optimization
Technical SEO is vital for mobile optimization, which directly impacts Core Web Vitals. With Google’s mobile-first indexing approach, ensuring that a site performs well on mobile devices is essential. This includes:
- Responsive Design: Implementing a responsive design ensures that content displays correctly across various screen sizes, improving user experience and potentially enhancing Core Web Vitals scores.
- Touch Targets: Ensuring buttons and links are appropriately sized for touch interactions can improve FID scores on mobile devices.
6. Regular Monitoring and Auditing
Technical SEO involves ongoing monitoring and auditing of website performance. Using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Search Console allows webmasters to identify issues related to Core Web Vitals and take corrective actions. Regular audits help ensure that technical SEO optimizations remain effective and that the site continues to perform well.
In, technical SEO is indeed a crucial part of optimizing for Core Web Vitals. By focusing on aspects like loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability through technical practices, website owners can significantly improve their Core Web Vitals scores. Given that these metrics directly impact user experience and search rankings, a robust technical SEO strategy is essential for achieving long-term success in the digital landscape. Prioritizing both technical SEO and Core Web Vitals optimization can lead to enhanced user satisfaction, better search visibility, and ultimately, improved business outcomes.
How Do Core Web Vitals Contribute to User Experience?
Core Web Vitals contribute to user experience by focusing on three critical aspects of how users interact with a webpage: loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. Here’s how each of the three metrics plays a role in enhancing user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
- Definition: LCP measures the loading performance of a webpage by tracking the time it takes for the largest visible content element (such as an image, video, or block of text) to load.
- User Experience Contribution: A fast LCP means users can access the main content of a page quickly. If a site loads slowly, users may become frustrated and leave before the content appears. Optimizing for LCP ensures that users see the essential content as soon as possible, making for a smoother and more satisfying experience.
- First Input Delay (FID):
- Definition: FID measures the time it takes for a webpage to become interactive after a user first interacts with it, such as clicking a button or a link.
- User Experience Contribution: A low FID indicates that users can engage with the page without delay. If there’s a long delay before the site responds to user input, it can lead to frustration and abandonment. Ensuring that interactions happen quickly helps maintain user engagement and satisfaction.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
- Definition: CLS measures visual stability by tracking how much the layout shifts during loading. A high CLS means elements on the page move around unexpectedly.
- User Experience Contribution: A low CLS ensures that users can interact with a webpage without elements shifting around them, which can be disorienting. For example, if a button moves just as a user is about to click it, it can lead to mistakes and frustration. A stable layout enhances usability and user confidence in interacting with the site.
Overall Impact on User Experience
- Reduced Frustration: Optimizing for these metrics reduces common frustrations users face, such as slow loading times, unresponsive interfaces, and layout shifts.
- Increased Satisfaction: A website that loads quickly, responds promptly, and maintains visual stability is more likely to leave users feeling satisfied and happy with their experience.
- Higher Engagement and Retention: Users are more likely to stay on a site that provides a good experience, leading to longer session durations and lower bounce rates. This can contribute to higher conversion rates and customer loyalty.
- Positive Brand Perception: A well-performing site reflects positively on a brand. Users are more likely to perceive a brand as professional and reliable if its website offers a smooth experience.
In ,Core Web Vitals are essential for creating a positive user experience. By focusing on loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, they help ensure that users can access and engage with content easily and enjoyably.
Key Metrics: Which Are the Most Important Core Web Vitals?

The most important Core Web Vitals metrics are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
- Definition: LCP measures the loading performance of a webpage by tracking the time it takes for the largest visible content element (like an image or a block of text) to load completely.
- Importance: A fast LCP ensures that users can see the main content of the page quickly, improving their initial impression and reducing the likelihood of abandonment. A good LCP score is under 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID):
- Definition: FID measures the time from when a user first interacts with a page (e.g., clicking a button or link) to when the browser can respond to that interaction.
- Importance: A low FID indicates that a page is interactive and responsive. If the delay is long, users may feel frustrated and may leave the site. A good FID score is under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
- Definition: CLS measures the visual stability of a webpage by tracking how much the layout shifts during the loading process.
- Importance: A low CLS score indicates a stable visual experience, preventing frustrating shifts that can lead to accidental clicks. A good CLS score is under 0.1.
Summary of Key Metrics
- LCP (Loading Performance): Aim for under 2.5 seconds.
- FID (Interactivity): Aim for under 100 milliseconds.
- CLS (Visual Stability): Aim for under 0.1.
These three metrics are critical for providing a good user experience and are used by Google as key indicators of page performance. Optimizing for these Core Web Vitals can lead to better user engagement, higher search engine rankings, and improved overall site performance.
What is LCP in Core Web Vitals?
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is a key metric in Google’s Core Web Vitals that measures the loading performance of a webpage. It specifically tracks the time it takes for the largest visible content element on the page to become fully visible in the viewport. This content element can be an image, video, or block of text.
Key Aspects of LCP:
- What It Measures: LCP captures how quickly the main content of a page is loaded and displayed to the user. This is crucial because it reflects the user’s perception of how fast the page is loading.
- Elements Considered: LCP considers various elements, including:
- Images (e.g., banners, thumbnails)
- Videos
- Large text blocks (e.g., headings)
- Good LCP Score: A good LCP score is under 2.5 seconds. Scores above this threshold indicate that users may experience delays in loading the main content, which can lead to frustration and increased bounce rates.
- Importance for User Experience:
- A fast LCP ensures that users can access the essential content quickly, enhancing their overall experience on the site.
- Slow loading times can result in users abandoning the page before it fully loads.
- Impact on SEO: Since LCP is a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, optimizing for this metric can help improve a website’s search engine rankings and visibility.
Improving LCP:
To enhance LCP performance, consider the following optimizations:
- Optimize Images: Use appropriately sized images and modern formats (like WebP) to reduce loading times.
- Server Response Time: Ensure the server responds quickly to requests by optimizing backend processes and using fast hosting solutions.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for off-screen images and videos to improve initial load times.
- Minimize Render-Blocking Resources: Reduce the number of CSS and JavaScript files that block rendering during the loading process.
In, LCP is a vital metric for measuring how quickly the largest content on a webpage is displayed, directly influencing user experience and SEO performance.
What is FID (First Input Delay) and Why It Matters?
First Input Delay (FID) is a key metric in Google’s Core Web Vitals that measures the responsiveness of a webpage. Specifically, it quantifies the time between a user’s first interaction with a page (such as clicking a button, tapping a link, or interacting with a form) and the browser’s response to that interaction.
Key Aspects of FID:
- What It Measures:
- FID captures the delay that users experience before they can engage with a webpage. It indicates how quickly a webpage becomes interactive after loading.
- Good FID Score:
- A good FID score is under 100 milliseconds. Scores above this threshold can lead to a frustrating experience for users, as they may feel like the page is unresponsive.
- Importance for User Experience:
- A low FID indicates a responsive site, meaning that users can interact with it smoothly. If the delay is long, users may become frustrated and leave the page, leading to a poor experience.
- Impact on User Engagement:
- Fast interactivity encourages users to stay longer, explore more, and engage with content. Conversely, high FID can increase bounce rates, as users are likely to abandon pages that feel sluggish.
- Impact on SEO:
- FID is a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm. Pages that provide a quick and responsive experience are more likely to rank higher in search results, thereby improving visibility and traffic.
Why FID Matters:
- User Expectations: Users expect fast and responsive interactions when they browse the web. A slow FID can lead to frustration, impacting user satisfaction and trust in the website.
- Conversion Rates: Websites that respond quickly to user interactions often see higher conversion rates, as users are more likely to complete desired actions (e.g., making purchases, signing up for newsletters) when the site feels responsive.
- Mobile Experience: With the rise of mobile browsing, FID is particularly important. Users on mobile devices may have different expectations for responsiveness, and delays can be even more pronounced on slower mobile networks.
Improving FID:
To enhance FID performance, consider the following optimizations:
- Reduce JavaScript Execution Time: Minimize the amount of JavaScript that needs to be executed on page load. Use code-splitting and defer or asynchronously load non-critical scripts.
- Optimize Page Load: Ensure that the main thread is not blocked by heavy tasks during page load. Optimize resources and minimize the use of large third-party scripts that can delay interactivity.
- Use Efficient Event Listeners: Optimize how events are handled on the page, ensuring that event listeners respond quickly without unnecessary delays.
- Prioritize Critical Resources: Load essential resources first to ensure that the user can interact with the page as soon as possible.
In, FID is a crucial metric that measures how quickly a webpage responds to user interactions. A low FID enhances user experience, encourages engagement, and can positively impact SEO performance. Optimizing for FID is essential for creating a responsive and user-friendly website.
What is CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) and How It Affects UX?
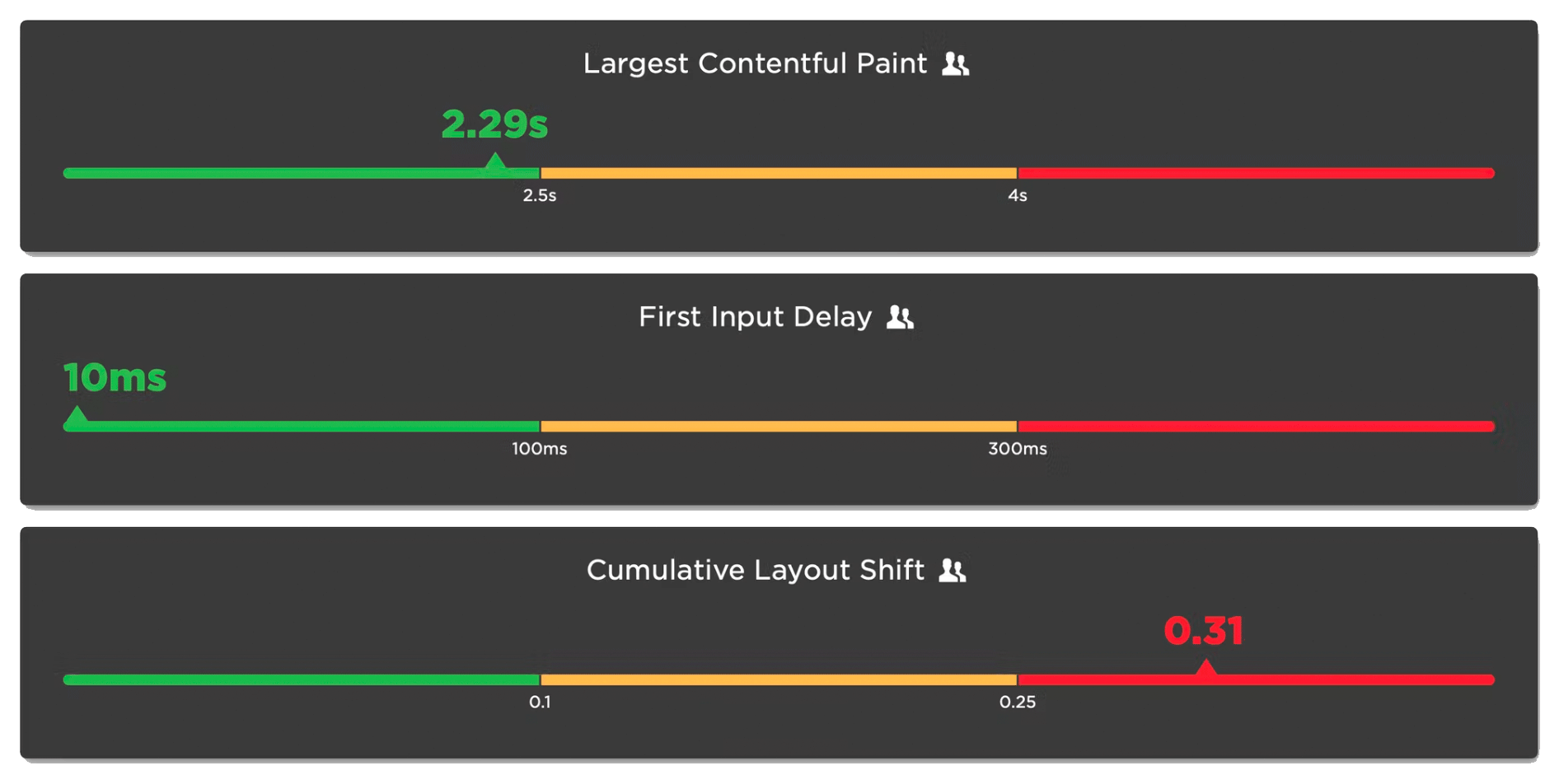
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is a key metric in Google’s Core Web Vitals that measures the visual stability of a webpage. It quantifies how much visible content shifts around on the page during loading. A high CLS score indicates that elements on the page move unexpectedly, which can lead to a frustrating user experience.
Key Aspects of CLS:
- What It Measures:
- CLS measures the total amount of unexpected layout shifts that occur while the page is loading. Each shift is calculated based on the size of the element that moved and the viewport size.
- Good CLS Score:
- A good CLS score is under 0.1. Scores above this threshold indicate that users may experience disruptive layout changes that can interfere with their interactions.
- Importance for User Experience:
- A low CLS ensures a stable visual experience. When users can interact with the page without elements shifting around, it enhances their overall satisfaction and reduces frustration.
- High CLS can lead to accidental clicks on buttons or links, causing users to navigate to unintended pages. This can be especially problematic for forms and interactive elements.
How CLS Affects User Experience (UX):
- Frustration and Confusion:
- When content shifts unexpectedly, it can confuse users and lead to frustration. For example, if a user is about to click a button that suddenly moves, they may end up clicking on the wrong link or element, which can be annoying.
- Negative Perception:
- A website that exhibits high layout shifts may be perceived as poorly designed or untrustworthy. This negative perception can affect user retention and brand reputation.
- Impact on Engagement:
- High CLS can increase bounce rates, as users are less likely to stay on a site that feels unstable. If users feel they can’t trust a site to remain consistent, they may leave before engaging with the content.
- Accessibility Concerns:
- For users with disabilities, unexpected layout shifts can create significant challenges in navigating a website. Consistent layouts help all users interact with content more effectively.
Improving CLS:
To enhance CLS performance, consider the following optimizations:
- Specify Size for Media:
- Always specify dimensions (width and height) for images, videos, and other media elements. This allows the browser to allocate space for these elements before they load, preventing shifts.
- Avoid Inserting Content Above Existing Content:
- When adding new elements to a page (like ads or pop-ups), ensure they don’t push down existing content. Instead, add them at the bottom of the page or reserve space for them.
- Use CSS for Layouts:
- Use CSS properties to define layouts rather than relying on JavaScript that might alter them after rendering. This can help maintain visual stability.
- Test and Monitor:
- Regularly test your website for CLS issues using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or the Lighthouse tool in Chrome DevTools. Monitor changes after implementing optimizations to ensure improvements.
In, CLS is a critical metric for assessing the visual stability of a webpage. A low CLS score contributes to a better user experience by ensuring that content remains stable during loading, reducing frustration, and enhancing user engagement. Prioritizing CLS optimization is essential for creating a user-friendly and reliable website.
How to Measure and Check Core Web Vitals?

Measuring and checking Core Web Vitals is essential for understanding how your website performs in terms of user experience. Here are several tools and methods you can use to measure Core Web Vitals effectively:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
- How to Use: Enter your website URL into the PageSpeed Insights tool.
- What It Provides: This tool provides a performance score along with detailed information on LCP, FID, and CLS. It also offers suggestions for improving your scores.
- Link: Google PageSpeed Insights
2. Lighthouse
- How to Use: Lighthouse is integrated into Chrome DevTools. Open DevTools (F12 or right-click → Inspect), go to the “Lighthouse” tab, and run an audit for your page.
- What It Provides: Lighthouse offers a comprehensive report on performance, including Core Web Vitals, accessibility, SEO, and best practices.
- Link: Lighthouse Documentation
3. Web Vitals Extension
- How to Use: Install the Web Vitals Chrome extension from the Chrome Web Store.
- What It Provides: This extension measures and displays LCP, FID, and CLS in real-time as you browse your website.
- Link: Web Vitals Extension
4. Google Search Console
- How to Use: If you have your site verified on Google Search Console, you can access the Core Web Vitals report.
- What It Provides: The report gives an overview of how your pages are performing in terms of LCP, FID, and CLS, categorizing pages as “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor.”
- Link: Google Search Console
5. Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
- How to Use: CrUX provides real user data collected from Chrome users. You can access it through the BigQuery or in the PageSpeed Insights tool.
- What It Provides: This report shows how real users experience your website in terms of Core Web Vitals, based on actual usage data.
- Link: Chrome User Experience Report
6. GTmetrix
- How to Use: Enter your URL into GTmetrix and run the test.
- What It Provides: GTmetrix offers performance scores, including Core Web Vitals, and provides recommendations for improvements.
- Link: GTmetrix
7. WebPageTest
- How to Use: Go to the WebPageTest website, enter your URL, and select test parameters.
- What It Provides: It provides in-depth performance analysis, including Core Web Vitals metrics, and allows testing from different locations and browsers.
- Link: WebPageTest
Summary of Measurement Tools:
- For Quick Insights: Google PageSpeed Insights, Web Vitals Extension
- For In-Depth Analysis: Lighthouse, GTmetrix, WebPageTest
- For Real User Data: Google Search Console, Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
Regular Monitoring:
To maintain optimal performance, regularly check your Core Web Vitals using these tools. Address any issues promptly to ensure a smooth user experience and to maintain or improve search engine rankings.
What Tools Can You Use to Monitor Core Web Vitals? (e.g., Core Web Vitals Checker, Monitoring Tools)
To check Core Web Vitals performance, you can use several tools and methods that provide insights into how well your website performs regarding the three key metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Here’s a step-by-step guide to checking Core Web Vitals performance:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
- Step-by-Step:
- Visit the Google PageSpeed Insights website.
- Enter your website URL in the provided field and click “Analyze.”
- Review the results, focusing on the Core Web Vitals section that displays LCP, FID, and CLS scores along with suggestions for improvements.
2. Lighthouse (in Chrome DevTools)
- Step-by-Step:
- Open your website in Google Chrome.
- Right-click anywhere on the page and select “Inspect” to open Chrome DevTools.
- Navigate to the “Lighthouse” tab.
- Choose the options you want (e.g., Mobile or Desktop) and click “Generate report.”
- Analyze the report, which includes detailed metrics for LCP, FID, and CLS, as well as recommendations for optimization.
3. Web Vitals Chrome Extension
- Step-by-Step:
- Install the Web Vitals Extension from the Chrome Web Store.
- Open your website in Chrome and click on the extension icon.
- The extension will display real-time metrics for LCP, FID, and CLS as you interact with your site.
4. Google Search Console
- Step-by-Step:
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Select your website property.
- In the left sidebar, click on “Core Web Vitals” under the “Enhancements” section.
- Review the report, which categorizes your pages as “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor” based on their Core Web Vitals performance.
5. Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
- Step-by-Step:
- Access CrUX data via BigQuery, or you can view it through tools like PageSpeed Insights.
- Analyze real user data for LCP, FID, and CLS, which provides insights based on actual user interactions with your site.
6. GTmetrix
- Step-by-Step:
- Go to GTmetrix.
- Enter your website URL and click “Test your site.”
- Review the performance report, focusing on the Core Web Vitals metrics and their scores along with suggestions for optimization.
7. WebPageTest
- Step-by-Step:
- Visit WebPageTest.
- Enter your URL and select test parameters such as location and browser.
- Run the test and analyze the detailed results, including Core Web Vitals metrics and a visual timeline of loading performance.
Monitoring and Regular Checks:
- Consistency: Regularly check your Core Web Vitals using these tools to monitor performance over time.
- Address Issues: If you notice any metrics falling below the recommended thresholds (LCP under 2.5 seconds, FID under 100 milliseconds, CLS under 0.1), take action to improve them.
By using these tools, you can effectively check your website’s Core Web Vitals performance, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the overall user experience. Regular monitoring will help you maintain optimal performance and improve your website’s search engine rankings.
How to Run a Core Web Vitals Audit for Your Site?
Running a Core Web Vitals audit for your website is essential to assess its performance and identify areas for improvement. A comprehensive audit helps you understand how well your site aligns with Google’s Core Web Vitals metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting a Core Web Vitals audit:
Step 1: Use Core Web Vitals Tools
Several tools can help you evaluate your site’s Core Web Vitals performance. The following are some of the most effective options:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- Enter your website URL to receive an overview of performance on both mobile and desktop.
- The tool provides scores for LCP, FID, and CLS, along with suggestions for improvement.
- Google Search Console
- Navigate to the “Core Web Vitals” report to see how your site performs over time and on various devices.
- This tool categorizes URLs into “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” and “Poor” based on their Core Web Vitals scores.
- Lighthouse
- Lighthouse is a built-in tool within Chrome Developer Tools that allows you to run audits for performance, accessibility, SEO, and more.
- Open the Chrome browser, go to your site, right-click, select “Inspect,” then go to the “Lighthouse” tab and generate a report.
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension
- This extension provides real-time feedback on Core Web Vitals as you browse your site.
- It helps monitor performance during various interactions and page loads.
Step 2: Analyze the Results
Once you’ve gathered data from the tools above, analyze the results to understand your site’s performance. Focus on the following metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Check if the loading time is 2.5 seconds or less. If it exceeds this, identify elements causing delays (e.g., large images or videos).
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Assess if the score is below 100 milliseconds. If users experience delays when interacting with your site, investigate any blocking JavaScript or heavy resources affecting responsiveness.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Look for a score below 0.1. If your site experiences significant layout shifts, identify elements that might be causing instability, such as ads or images without defined dimensions.
Step 3: Identify Improvement Opportunities
Based on your analysis, pinpoint specific areas for improvement. Here are common issues and their corresponding fixes:
- Improve LCP:
- Optimize images by compressing them and using next-gen formats (like WebP).
- Use lazy loading for off-screen images to speed up initial loading times.
- Minimize server response times by leveraging caching and using a reliable hosting provider.
- Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to deliver content faster to users worldwide.
- Enhance FID:
- Optimize JavaScript files by minimizing their size and deferring non-essential scripts to reduce load on the main thread.
- Break up long tasks into smaller ones to ensure the page remains responsive.
- Remove any third-party scripts that may block rendering.
- Reduce CLS:
- Always specify dimensions for images and videos to ensure the browser reserves space before they load.
- Avoid using dynamically injected content (like ads) that can cause shifts. Instead, reserve space for ads or use placeholders.
Step 4: Implement Changes and Re-Test
After identifying areas for improvement, implement the necessary changes to your website. Once updates are made, re-run the Core Web Vitals audit using the same tools. This will help you evaluate whether the optimizations have resulted in better scores.
Step 5: Monitor Performance Over Time
Core Web Vitals performance can fluctuate based on various factors, including new content, changes in user behavior, or updates to your website. Regular monitoring is crucial. Use Google Search Console to keep an eye on your Core Web Vitals report and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 6: Continuously Optimize
Core Web Vitals should not be viewed as a one-time effort. As your website evolves, new challenges may arise. Regularly audit your site’s performance, stay updated on the latest web development practices, and make continuous improvements to enhance user experience and maintain strong search rankings.
Running a Core Web Vitals audit is an essential practice for any website owner looking to improve user experience and search engine performance. By utilizing the right tools, analyzing results, identifying improvement opportunities, and implementing changes, you can optimize your site’s performance on Core Web Vitals metrics. Continuous monitoring and optimization will ensure your website remains competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Core Web Vitals Optimization Strategies: How to Improve and Fix Issues
Improving Core Web Vitals is essential for enhancing user experience and boosting your website’s SEO performance. Here are optimization strategies tailored for each of the three key metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Strategies to Improve LCP (Largest Contentful Paint)
- Optimize Images:
- Use appropriate formats (e.g., WebP for web images).
- Compress images without sacrificing quality to reduce loading times.
- Serve images in responsive sizes (using srcset or CSS) to ensure the right size loads on different devices.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN):
- Distribute content across multiple servers to reduce latency and improve loading times for users in different geographical locations.
- Minimize Server Response Time:
- Optimize your backend performance (e.g., database queries, server configuration).
- Consider using faster hosting services or upgrading your current plan.
- Preload Key Resources:
- Use <link rel=”preload”> to load critical resources (like fonts or images) early in the page load process.
- Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources:
- Defer or asynchronously load non-critical JavaScript and CSS to prevent blocking the rendering of the main content.
Strategies to Improve FID (First Input Delay)
- Optimize JavaScript Execution:
- Minimize the amount of JavaScript loaded on initial page load. Use code-splitting to load only the essential scripts.
- Reduce the execution time of scripts by removing unused code or libraries.
- Use Web Workers:
- Offload non-urgent JavaScript tasks to web workers, allowing the main thread to remain responsive for user interactions.
- Reduce the Impact of Third-Party Scripts:
- Limit the use of third-party scripts that can block the main thread. Consider loading them asynchronously or deferring them until after the initial user interaction.
- Implement Efficient Event Handlers:
- Optimize event handlers to ensure they are lightweight and do not block the main thread.
Strategies to Improve CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift)
- Set Size for Media Elements:
- Always specify width and height for images, videos, and other media elements to reserve space in the layout before they load.
- Avoid Inserting Content Above Existing Content:
- Be cautious when adding new elements to the page. Ensure that new content (like ads or pop-ups) is added below existing content, or reserve space for it.
- Use CSS for Layouts:
- Define layouts with CSS properties (e.g., Flexbox or Grid) to maintain stability as elements load.
- Implement Font Loading Strategies:
- Use the font-display: swap; property to avoid layout shifts caused by font loading. This allows text to be displayed with a fallback font until the custom font is loaded.
- Monitor and Optimize Third-Party Scripts:
- Regularly check and optimize the impact of third-party scripts, such as ads, embeds, or social media widgets, to minimize layout shifts.
General Best Practices
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor Core Web Vitals using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Web Vitals Extension to identify new issues and track improvements.
- Conduct A/B Testing: Test changes on a subset of users to see the impact of optimizations on Core Web Vitals and overall user experience.
- Prioritize Mobile Optimization: With mobile traffic on the rise, ensure that your optimizations are effective across all devices and screen sizes.
- Use Performance Budgets: Set performance budgets for Core Web Vitals metrics to guide development and design decisions.
Improving Core Web Vitals requires a combination of technical optimizations, efficient resource management, and ongoing monitoring. By implementing these strategies, you can enhance user experience, reduce bounce rates, and improve your site’s visibility in search engine results. Regularly reviewing performance and making iterative improvements will help maintain a high standard of web performance.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals: Best Practices
Improving Core Web Vitals is crucial for delivering a better user experience and enhancing your site’s SEO performance. Here are some best practices to effectively optimize each of the Core Web Vitals metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Best Practices for Improving Core Web Vitals
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Optimize Images:
- Use Next-Gen Formats: Implement image formats like WebP or AVIF, which offer better compression without loss of quality.
- Responsive Images: Utilize srcset and the <picture> element to deliver appropriately sized images for different devices and screen resolutions.
- Lazy Load Off-Screen Images: Implement lazy loading for images that are not immediately visible to reduce initial load times.
- Server Optimization:
- Fast Hosting Solutions: Choose high-performance hosting options or consider upgrading your current plan for faster server response times.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute your content across various locations to reduce latency and improve loading speeds for users worldwide.
- Preload Important Resources:
- Use <link rel=”preload”> for critical resources (like hero images or CSS) to prioritize their loading.
- Reduce Render-Blocking Resources:
- Minimize the use of blocking JavaScript and CSS. Use asynchronous or deferred loading for scripts and inline critical CSS.
2. First Input Delay (FID)
- Optimize JavaScript:
- Minimize JavaScript Execution Time: Remove unnecessary scripts and reduce the size of critical scripts. Consider code-splitting to load only essential code upfront.
- Defer Non-Critical JavaScript: Load less important scripts after the main content has loaded to keep the main thread available for user interactions.
- Use Web Workers:
- Offload heavy computations to web workers, which run scripts in the background without blocking the main thread.
- Efficient Event Handling:
- Use event delegation and ensure event handlers are lightweight. Avoid using long-running tasks in event listeners.
- Optimize Third-Party Scripts:
- Limit the use of third-party libraries and load them asynchronously to avoid blocking interactions.
3. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Set Size for Media Elements:
- Specify Dimensions: Always define the width and height attributes for images and video elements. This helps the browser allocate space before the content loads.
- Avoid Content Shifting:
- Be mindful of how you insert content into the page. Avoid placing new elements above existing content, which can cause layout shifts.
- Use CSS to Maintain Layout Stability:
- Implement CSS layout techniques such as Flexbox or Grid to create stable layouts that don’t shift as elements load.
- Font Loading Strategy:
- Implement font-display: swap; in your CSS to ensure text is displayed immediately with fallback fonts, reducing layout shifts caused by late-loading fonts.
- Monitor and Manage Third-Party Content:
- Regularly review third-party scripts and ads to minimize their impact on layout stability. Ensure that they reserve appropriate space in your layout.
General Best Practices
- Regularly Monitor Performance: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and the Web Vitals Extension to continuously monitor Core Web Vitals performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Conduct A/B Testing: Test changes on a subset of your audience to evaluate the impact of optimizations on user experience and performance metrics.
- Optimize for Mobile Devices: Ensure your site is responsive and performs well on mobile devices, as mobile users often experience different loading times and interactions.
- Establish Performance Budgets: Set performance budgets for LCP, FID, and CLS to guide your development and design processes, ensuring that you maintain focus on user experience.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Use caching strategies to store frequently accessed resources, reducing load times for returning visitors.
By following these best practices, you can effectively improve your Core Web Vitals metrics, leading to enhanced user experience, lower bounce rates, and better search engine rankings. Continuous monitoring and iterative improvements will help maintain high performance over time, ensuring your website meets the expectations of users and search engines alike.
How to Fix Core Web Vitals Issues on Your Site?
Fixing Core Web Vitals issues on your site is essential for enhancing user experience and improving SEO performance. Here’s a comprehensive guide on identifying and resolving common issues related to the three Core Web Vitals metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Steps to Fix Core Web Vitals Issues
1. Fixing LCP (Largest Contentful Paint)
- Optimize Images:
- Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce the file size of images without losing quality.
- Use Appropriate Formats: Implement next-gen formats like WebP or AVIF for better compression and faster loading.
- Responsive Images: Use the <picture> element or the srcset attribute to serve different image sizes based on the user’s device.
- Improve Server Response Times:
- Upgrade Hosting: Consider switching to a faster hosting provider or upgrading your existing plan to improve server performance.
- Use a CDN: Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to reduce latency by serving content from a location closer to the user.
- Minimize Render-Blocking Resources:
- Defer or Async Load JavaScript: Modify script tags to load non-critical JavaScript asynchronously or defer loading until after the main content is rendered.
- Inline Critical CSS: Inline critical CSS to ensure essential styles are loaded first, which helps render content faster.
- Preload Key Resources:
- Use <link rel=”preload”> for critical images or fonts to load them earlier in the page load process.
2. Fixing FID (First Input Delay)
- Reduce JavaScript Execution Time:
- Code Splitting: Break down large JavaScript files into smaller chunks that can be loaded as needed.
- Minimize JavaScript: Remove unused JavaScript and reduce the overall size of your scripts using tools like UglifyJS or Terser.
- Use Web Workers:
- Offload heavy tasks to web workers, which can perform background operations without blocking the main thread.
- Optimize Event Handlers:
- Use efficient event delegation and ensure event handlers are lightweight. Avoid long-running tasks within event listeners.
- Limit Third-Party Scripts:
- Review and minimize the use of third-party scripts that can block the main thread. Load them asynchronously or defer them.
3. Fixing CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift)
- Specify Dimensions for Media:
- Always set explicit width and height for images and video elements. This ensures that space is reserved for them before they load.
- Avoid Inserting Content Above Existing Content:
- Be cautious when adding new elements (like ads or pop-ups). Make sure they do not push down existing content.
- Use CSS to Maintain Layout:
- Implement CSS techniques such as Flexbox or Grid to create stable layouts that prevent shifting as content loads.
- Implement Font Loading Strategies:
- Use font-display: swap; to ensure text is displayed with a fallback font while the custom font loads, reducing layout shifts.
- Manage Third-Party Content:
- Regularly review and optimize third-party scripts, ads, and embeds to minimize their impact on layout stability.
Tools to Identify Core Web Vitals Issues
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Provides detailed reports on your site’s Core Web Vitals and suggests specific improvements.
- Lighthouse: Integrated into Chrome DevTools, it offers insights and recommendations for optimizing performance.
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension: Allows you to monitor Core Web Vitals metrics in real-time as you browse your site.
- Google Search Console: Offers a report on your site’s Core Web Vitals, categorizing pages based on performance.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Regular Checks: Make it a habit to regularly check your Core Web Vitals metrics using the tools mentioned above to identify new issues.
- Iterative Improvements: Apply changes incrementally and test the impact of each change on Core Web Vitals performance.
- User Feedback: Collect user feedback to understand how changes affect their experience on your site.
Addressing Core Web Vitals issues requires a combination of technical optimizations and ongoing monitoring. By following the steps outlined above, you can enhance your website’s performance, improve user satisfaction, and positively impact your search engine rankings.
How to Optimize Core Web Vitals Through Mobile Responsiveness?
Optimizing Core Web Vitals through mobile responsiveness is crucial for ensuring a positive user experience on mobile devices. With a growing number of users accessing websites via smartphones and tablets, a responsive design can significantly impact your site’s performance metrics, including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Here are some effective strategies to enhance mobile responsiveness and optimize Core Web Vitals:
1. Implement Responsive Design
- Fluid Grids and Layouts: Use CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Flexbox to create fluid layouts that adapt to different screen sizes. This ensures that content scales properly without causing layout shifts.
- Media Queries: Utilize media queries in your CSS to apply different styles based on screen size. This helps maintain a consistent design across devices.
2. Optimize Images for Mobile
- Responsive Images: Use the <picture> element or the srcset attribute to serve appropriately sized images based on the device’s resolution and size.
- Image Compression: Optimize images by compressing them without sacrificing quality. Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim can help reduce file sizes for faster loading times.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and videos to defer loading of off-screen content until it is needed. This can significantly improve LCP.
3. Improve Loading Times
- Minimize Resource Size: Compress CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their size, which helps speed up loading times. Tools like Gzip or Brotli can be used for compression.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN can deliver your content from servers located closer to users, reducing latency and improving loading speeds.
4. Enhance Server Response Times
- Fast Hosting Solutions: Choose a high-performance hosting provider that can handle mobile traffic efficiently. Consider options like managed WordPress hosting or VPS for better performance.
- Reduce Server Response Time: Optimize your backend by improving database queries, reducing the size of server responses, and eliminating unnecessary redirects.
5. Minimize JavaScript Execution Time
- Asynchronous Loading: Load non-critical JavaScript files asynchronously or defer them until after the main content is rendered to improve FID.
- Code Splitting: Break down large JavaScript files into smaller, manageable chunks to reduce the initial loading time.
6. Optimize Touch Target Sizes
- Adequate Touch Targets: Ensure buttons and interactive elements are large enough (at least 48×48 pixels) and spaced adequately to prevent accidental clicks, improving usability and FID.
- Avoid Pop-ups and Interstitials: Minimize the use of intrusive pop-ups that can disrupt the user experience, especially on mobile devices.
7. Manage Third-Party Scripts
- Limit Third-Party Requests: Review and minimize the use of third-party scripts, as they can significantly impact performance. Only include essential scripts and load them asynchronously.
- Use Performance Monitoring Tools: Regularly assess the impact of third-party scripts on Core Web Vitals using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse.
8. Test and Iterate
- Regular Testing: Continuously test your website’s performance on various mobile devices and screen sizes using tools like BrowserStack or Responsinator.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from users regarding their mobile experience and make iterative improvements based on their suggestions.
9. Monitor Core Web Vitals
- Use Analytics Tools: Regularly check your site’s Core Web Vitals metrics through Google PageSpeed Insights, Google Search Console, and other performance monitoring tools.
- Implement Monitoring Solutions: Consider using real user monitoring (RUM) tools to gather data on how users experience your site on different devices.
By focusing on mobile responsiveness and implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve your Core Web Vitals scores. A mobile-optimized site enhances user experience, reduces bounce rates, and boosts your website’s search engine rankings. Regular testing and monitoring are essential to maintain optimal performance as technologies and user expectations evolve.
How to Prepare for Core Web Vitals Updates?
Preparing for Core Web Vitals updates is essential for website owners and SEO professionals looking to maintain or improve their search rankings and ensure a positive user experience. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to effectively prepare for these updates:
1. Understand Core Web Vitals Metrics
Before preparing for updates, it’s crucial to understand the Core Web Vitals metrics and their significance:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance; it should be 2.5 seconds or less.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity; it should be less than 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability; a score of less than 0.1 is ideal.
Stay informed about these metrics and their thresholds to understand what you need to optimize.
2. Regularly Monitor Your Site’s Performance
To stay ahead of Core Web Vitals updates, consistently monitor your website’s performance:
- Use Google Search Console: Check the “Core Web Vitals” report regularly to identify any URLs that are flagged as “Poor” or “Needs Improvement.”
- Leverage Tools: Utilize tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Web Vitals Chrome Extension to get real-time feedback on your Core Web Vitals performance.
By monitoring performance regularly, you can spot potential issues before they become significant problems.
3. Perform a Comprehensive Site Audit
Conduct a thorough audit of your website to identify areas needing improvement:
- Check Loading Speed (LCP): Analyze elements contributing to slow loading times, such as large images, scripts, or server response times.
- Assess Interactivity (FID): Evaluate JavaScript execution and identify any blocking scripts that may delay user interactions.
- Evaluate Visual Stability (CLS): Identify elements causing layout shifts, such as ads or images without specified dimensions.
Tools like Google Lighthouse can help automate this process, providing insights into where improvements are needed.
4. Implement Best Practices for Optimization
After identifying issues, implement best practices to enhance your Core Web Vitals scores:
- Optimize Images and Videos: Compress files, use next-gen formats (like WebP), and implement lazy loading for off-screen content.
- Minimize JavaScript Blocking: Reduce the size of JavaScript files, defer non-critical scripts, and break long tasks into smaller ones to improve responsiveness.
- Use CSS for Layout Stability: Ensure all images have defined dimensions and avoid using dynamic content that may cause layout shifts.
By adhering to these best practices, you can proactively enhance your Core Web Vitals scores.
5. Stay Updated on Google’s Guidelines
Google frequently updates its algorithms and guidelines regarding Core Web Vitals. Keep yourself informed by:
- Following Google’s Official Blog: Google often announces changes, updates, and new best practices on its blog.
- Engaging with the SEO Community: Join forums, webinars, and online groups where industry experts discuss changes and share insights.
Staying informed will help you adapt your strategies in response to updates.
6. Conduct A/B Testing
Before and after making changes, conduct A/B testing to see how optimizations affect your Core Web Vitals scores and user engagement. Testing allows you to compare different strategies and determine the most effective approaches for your audience.
7. Educate Your Team
If you work with a team, ensure that everyone understands the importance of Core Web Vitals and their impact on user experience and SEO. Provide training or resources to keep your team informed about best practices and any updates related to Core Web Vitals.
8. Prepare for Future Updates
Since Google is likely to continue evolving its metrics and ranking factors, maintain a proactive mindset. Here are a few ways to stay prepared:
- Implement Continuous Monitoring: Utilize automated tools to continually track Core Web Vitals scores and alert you to potential issues.
- Adapt Your SEO Strategy: Incorporate Core Web Vitals into your overall SEO strategy, ensuring they align with your content and technical SEO efforts.
- Focus on User Experience: Always prioritize user experience in your website design
- and content strategy, as this will help you remain resilient to future updates.
Preparing for Core Web Vitals updates is an ongoing process that involves understanding the metrics, monitoring performance, implementing best practices, and staying informed about changes in Google’s guidelines. By taking proactive steps and continuously optimizing your website, you can enhance user experience, improve search rankings, and ensure your site remains competitive in the ever-evolving digital landscape. Ultimately, a strong focus on Core Web Vitals will lead to greater user satisfaction, increased engagement, and better business outcomes.
When is the Core Web Vitals Update?
The Core Web Vitals update, which focuses on user experience signals as ranking factors, began rolling out on June 15, 2021. This update integrates Core Web Vitals metrics—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—into Google’s ranking algorithms.
Key Points About the Update:
- Rollout Timeline: The update started on June 15, 2021, and was completed by the end of August 2021. This phased rollout allowed Google to monitor the impact and adjust as needed.
- Impact on Rankings: Websites that provide a better user experience based on these metrics may see improvements in their search rankings. Conversely, sites with poor performance on these metrics could experience a drop in visibility.
- Continuous Updates: Google emphasizes that Core Web Vitals will be updated regularly to adapt to evolving user expectations and technological advancements. It’s crucial for website owners to continuously monitor and optimize their Core Web Vitals scores.
- Resource Availability: Google has provided resources and tools (such as PageSpeed Insights, Google Search Console, and Lighthouse) to help webmasters understand and improve their Core Web Vitals performance.
Future Considerations
While the initial update has been rolled out, Google has indicated that user experience will continue to play a significant role in search ranking algorithms. It’s essential for website owners to stay informed about any future updates or changes related to Core Web Vitals to maintain optimal performance and user experience.
What Should You Know About Google’s New Core Web Vitals Metrics?
Google’s Core Web Vitals metrics represent a shift in how user experience is measured and evaluated in the context of search rankings. Here’s what you should know about these metrics:
1. Definition of Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals consist of three specific metrics that focus on user experience as a critical component of web performance:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. It assesses how long it takes for the largest visible content element (like an image or text block) to load on the screen. Ideally, LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of when the page starts loading.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. It quantifies the time from when a user first interacts with a page (like clicking a button) to when the browser begins processing that interaction. A good FID is less than 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. It tracks how much the page layout shifts during loading. A CLS score of less than 0.1 is considered good, indicating minimal unexpected layout shifts.
2. Importance of Core Web Vitals
- User Experience: Google emphasizes that these metrics directly correlate with user experience. Pages that load quickly and respond to user interactions promptly will provide a better overall experience.
- SEO Ranking Factor: As of the June 2021 update, Core Web Vitals are included in Google’s ranking algorithm, meaning that sites performing well in these areas may gain a ranking advantage.
- Shift Towards User-Centric Metrics: This change signifies a broader trend in search engine optimization, moving towards metrics that reflect real user interactions rather than purely technical aspects of website performance.
3. How to Measure Core Web Vitals
- Google PageSpeed Insights: This tool provides a report on how well your page performs based on Core Web Vitals, along with suggestions for improvement.
- Google Search Console: The Core Web Vitals report in Search Console offers an overview of how your website is performing across all pages and highlights issues that need attention.
- Lighthouse: Integrated into Chrome DevTools, Lighthouse can be used to audit a page’s performance and gives insights into Core Web Vitals.
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension: This extension allows real-time monitoring of Core Web Vitals metrics while browsing.
4. Strategies for Improvement
- Optimize Loading Performance (LCP):
- Compress and optimize images and use modern formats (like WebP).
- Serve critical resources via a CDN.
- Minimize render-blocking resources by deferring non-essential scripts.
- Enhance Interactivity (FID):
- Reduce JavaScript execution time by optimizing code and using code-splitting.
- Load scripts asynchronously to prevent blocking the main thread.
- Improve Visual Stability (CLS):
- Set explicit width and height for images and videos.
- Avoid dynamically inserting content above existing elements to prevent unexpected layout shifts.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Updates
- Ongoing Assessment: Regularly check your Core Web Vitals using the mentioned tools to ensure your website maintains optimal performance as new content and features are added.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates from Google regarding Core Web Vitals, as they may refine their approach or introduce new metrics in the future.
Understanding and optimizing for Google’s Core Web Vitals is essential for improving user experience and maintaining competitive search rankings. By focusing on loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability, you can create a better experience for your users, which is increasingly recognized and rewarded by search engines. Regular monitoring and adjustments based on performance data will help sustain these improvements over time.
Core Web Vitals Optimization Services and Tools
As businesses strive to enhance user experience and boost search engine rankings, optimizing Core Web Vitals has become a critical focus. Core Web Vitals—comprising Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—are vital metrics that impact how users perceive a website. To help businesses achieve optimal performance, various services and tools are available for Core Web Vitals optimization. Here’s a comprehensive overview.
1. Understanding Core Web Vitals
Before diving into optimization services and tools, it’s essential to grasp the importance of Core Web Vitals:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. A good LCP score is 2.5 seconds or less, indicating that the main content of the page is loaded quickly.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. A score of less than 100 milliseconds is ideal, reflecting how quickly the page responds to user interactions.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. A score under 0.1 indicates that the layout is stable, preventing unexpected shifts during loading.
2. Core Web Vitals Optimization Services
Various services are available to help businesses optimize their websites for Core Web Vitals. Here are some key offerings:
-
Website Performance Audits:
- Comprehensive evaluations of website performance metrics, including Core Web Vitals.
- Identification of issues affecting LCP, FID, and CLS.
- Actionable recommendations for optimization.
-
Performance Optimization Consulting:
- Expert consultation to develop tailored strategies for improving Core Web Vitals.
- In-depth analysis of technical SEO aspects and how they affect Core Web Vitals.
-
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Integration:
- Implementing a CDN to enhance site speed and improve LCP by delivering content faster to users across the globe.
-
Image and Video Optimization:
- Services to compress images, implement lazy loading, and convert media to next-gen formats, enhancing loading performance and reducing CLS.
-
JavaScript Optimization:
- Minimizing and deferring non-essential JavaScript to enhance FID and interactivity.
- Code splitting and removing blocking scripts to improve loading times.
-
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Ongoing monitoring of Core Web Vitals to identify any performance dips and implement corrective measures.
- Regular updates and performance assessments to ensure optimal site functionality.
3. Core Web Vitals Optimization Tools
In addition to services, several tools can help assess and improve Core Web Vitals:
- Google PageSpeed Insights:
- An essential tool that analyzes web pages and provides insights into their performance.
- Offers scores for LCP, FID, and CLS, along with specific suggestions for improvement.
- Google Search Console:
- Provides a dedicated Core Web Vitals report to track how URLs perform based on real-world data.
- Identifies issues and provides recommendations for improving Core Web Vitals.
- Lighthouse:
- A powerful open-source tool built into Chrome DevTools that audits web pages for performance, accessibility, SEO, and more.
- Generates reports focusing on Core Web Vitals metrics.
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension:
- A simple extension that provides real-time feedback on Core Web Vitals as you browse any site.
- Helps monitor performance directly during user interactions.
- GTmetrix:
- A robust tool that analyzes the loading performance of web pages and provides detailed reports, including Core Web Vitals metrics.
- Offers actionable insights and recommendations for optimization.
- Pingdom:
- A performance monitoring tool that tests the load time of your website from different locations.
- Provides insights into various performance metrics, including Core Web Vitals.
4. Best Practices for Core Web Vitals Optimization
When leveraging optimization services and tools, it’s important to follow best practices:
- Optimize Images and Videos: Compress images, use appropriate formats, and implement lazy loading to enhance loading times and reduce CLS.
- Minimize JavaScript: Reduce the size of JavaScript files, defer non-essential scripts, and ensure efficient loading to improve FID.
- Improve Server Response Times: Optimize server performance to decrease loading times and improve LCP. Consider upgrading your hosting plan if necessary.
- Implement Caching: Use browser caching and server-side caching to enhance loading speed for returning visitors.
- Test Regularly: Continuously test your website using various tools to track performance and identify areas needing improvement.
Optimizing Core Web Vitals is essential for enhancing user experience and improving search rankings. By utilizing specialized services and effective tools, businesses can identify and address performance issues, ensuring that their websites load quickly, respond promptly, and maintain visual stability. Adopting best practices and continuously monitoring performance will ultimately lead to better user satisfaction, increased engagement, and higher conversion rates. As Google continues to emphasize the importance of Core Web Vitals, investing in optimization will position your website for success in the competitive digital landscape.
What is a Core Web Vitals Optimization Service?
A Core Web Vitals Optimization Service is a specialized service offered by digital marketing or web development agencies aimed at improving a website’s performance metrics related to Google’s Core Web Vitals. These metrics—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—are critical for ensuring a positive user experience and enhancing search engine rankings.
Key Features of Core Web Vitals Optimization Services
- Performance Audits:
- Conduct thorough audits of your website to evaluate its current performance against Core Web Vitals benchmarks.
- Identify specific areas that need improvement, such as loading speed, interactivity, and layout stability.
- Technical Optimization:
- Optimize website assets, including images, CSS, and JavaScript, to reduce loading times and enhance performance.
- Implement caching strategies, content delivery networks (CDNs), and other server optimizations to improve server response times.
- User Experience Improvements:
- Analyze user interactions to enhance the website’s interactivity and responsiveness, thereby improving FID.
- Make layout changes to ensure visual stability, thereby reducing CLS. This includes setting explicit dimensions for media and avoiding unexpected layout shifts.
- Mobile Optimization:
- Ensure that the website is fully responsive and performs well on mobile devices, which is critical since mobile users often have different performance needs compared to desktop users.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting:
- Provide continuous monitoring of Core Web Vitals performance through tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Google Search Console.
- Generate regular reports that outline improvements made, ongoing issues, and recommendations for further enhancements.
- Custom Strategies:
- Develop tailored strategies based on the specific needs of your website and its audience, focusing on achieving optimal Core Web Vitals scores.
- Incorporate SEO strategies alongside performance optimizations to maximize the impact on search rankings.
- Consultation and Support:
- Offer expert advice on best practices for maintaining and improving Core Web Vitals as web technologies and standards evolve.
- Provide support for implementing recommendations and addressing any technical challenges that arise.
Benefits of Using a Core Web Vitals Optimization Service
- Improved User Experience: A well-optimized website provides a faster, smoother experience for users, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement rates.
- Better Search Rankings: With Core Web Vitals becoming an integral part of Google’s ranking algorithms, improving these metrics can enhance your site’s visibility in search results.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: Faster loading times and interactive elements reduce the likelihood of users leaving your site due to poor performance.
- Higher Conversion Rates: An optimized site can lead to increased conversions, as users are more likely to engage with a site that performs well.
- Expert Knowledge: Working with professionals who specialize in Core Web Vitals ensures that you benefit from the latest techniques and technologies in web optimization.
A Core Web Vitals Optimization Service is an invaluable resource for businesses looking to enhance their website’s performance, user experience, and search engine rankings. By leveraging specialized expertise, businesses can effectively address the technical challenges associated with Core Web Vitals and create a more user-friendly online presence.
Core Web Vitals Monitoring Solutions for Long-Term Success
In today’s digital landscape, optimizing for Core Web Vitals has become essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Core Web Vitals—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—are key metrics that significantly influence user experience and search engine rankings. However, achieving optimal performance is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Here’s a look at effective Core Web Vitals monitoring solutions that can lead to long-term success.
1. Understanding the Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Core Web Vitals metrics are dynamic and can fluctuate based on various factors, including changes in content, user behavior, and updates to web technology. Continuous monitoring is vital for several reasons:
- Immediate Identification of Issues: Monitoring helps you quickly detect performance issues that can negatively impact user experience and SEO rankings.
- Informed Decision-Making: Regular performance data enables you to make data-driven decisions regarding optimizations and adjustments.
- Adaptation to Changes: As website technology evolves and user expectations change, continuous monitoring allows you to adapt your strategies accordingly.
2. Core Web Vitals Monitoring Solutions
Various tools and solutions are available to help businesses continuously monitor Core Web Vitals performance:
- Google Search Console:
- Offers a dedicated Core Web Vitals report that highlights issues affecting your URLs based on real user data.
- Provides insights into how your website performs across different devices, helping you identify specific areas for improvement.
- Google PageSpeed Insights:
- Analyzes your website’s performance and provides scores for LCP, FID, and CLS.
- Offers recommendations for optimization, enabling you to implement changes and monitor the impact over time.
- Lighthouse:
- A powerful open-source tool that provides detailed audits of web pages, focusing on performance, accessibility, SEO, and best practices.
- Can be run as a Chrome DevTools feature or through the command line, making it a versatile option for monitoring Core Web Vitals.
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension:
- This handy extension provides real-time monitoring of Core Web Vitals as you navigate your website.
- It helps you understand the performance metrics directly in the browser, enabling you to spot issues instantly.
- GTmetrix:
- Offers in-depth performance analysis, including Core Web Vitals metrics.
- Provides actionable insights and detailed reports to help you optimize your website effectively.
- Pingdom:
- A performance monitoring tool that tests your website’s loading speed and performance from various locations around the globe.
- Tracks historical performance data, allowing you to identify trends and make informed decisions about optimizations.
- Dynatrace:
- A comprehensive monitoring solution that tracks application performance, user interactions, and Core Web Vitals in real-time.
- Offers AI-driven insights to help you pinpoint performance bottlenecks and optimize user experience.
3. Setting Up Effective Monitoring Processes
To maximize the benefits of Core Web Vitals monitoring, it’s essential to establish effective processes:
- Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish specific KPIs related to Core Web Vitals to help you measure success and track improvements over time.
- Schedule Regular Checks: Implement a routine for monitoring Core Web Vitals, whether through automated tools or manual checks, to ensure consistent performance assessment.
- Create Alerts for Performance Drops: Utilize monitoring tools that allow you to set alerts for significant drops in performance metrics. This enables swift action to address issues before they impact users.
- Conduct Regular Performance Reviews: Periodically review performance data and metrics with your team to assess progress and discuss areas for improvement.
4. Utilizing Data for Long-Term Strategy Development
Continuous monitoring generates valuable data that can inform your long-term strategy:
- Identify Trends: Analyze historical data to identify patterns in performance metrics over time, helping you understand what optimizations yield the best results.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Compare your Core Web Vitals scores against industry benchmarks or competitors to assess your position in the market and identify areas needing attention.
- Test New Implementations: Use A/B testing to measure the impact of new features or optimizations on Core Web Vitals scores, helping you refine your approach for maximum effectiveness.
5. Fostering a Culture of Performance Awareness
To achieve long-term success, it’s crucial to foster a culture of performance awareness within your organization:
- Educate Your Team: Provide training and resources to help your team understand the importance of Core Web Vitals and their impact on user experience and SEO.
- Involve Stakeholders: Ensure that all stakeholders, including developers, designers, and content creators, understand how their work influences Core Web Vitals performance.
- Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge improvements in Core Web Vitals metrics to motivate your team and encourage a continued focus on performance optimization.
Core Web Vitals monitoring is essential for achieving and maintaining optimal website performance, leading to enhanced user experiences and improved search rankings. By leveraging a combination of monitoring tools, establishing effective processes, utilizing data for strategic decisions, and fostering a performance-aware culture, businesses can ensure long-term success in optimizing Core Web Vitals. In an era where user expectations are continually evolving, proactive monitoring and adaptation are key to staying competitive in the digital landscape.
How Core Web Vitals Can Boost Your Website’s SEO Success
In today’s digital landscape, user experience plays a critical role in determining a website’s success. Google’s Core Web Vitals—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—serve as essential metrics that reflect this user experience. Focusing on these metrics can significantly enhance your website’s performance, ultimately boosting its visibility and rankings in search engine results.
Why Focusing on Core Web Vitals is Important for Growth
- User-Centric Approach: Core Web Vitals prioritize real user experiences, moving beyond traditional SEO metrics to emphasize how users interact with and perceive your site. A site that loads quickly, responds promptly to interactions, and maintains visual stability fosters a more positive experience.
- Search Engine Rankings: With Google incorporating Core Web Vitals into its ranking algorithms, optimizing for these metrics is essential for improving search visibility. Websites that perform well on these metrics are more likely to rank higher in search results, attracting more organic traffic.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: Improving load times and interactivity decreases the likelihood of users leaving your site due to frustration. A seamless experience encourages users to stay longer, explore your content, and engage with your offerings.
- Enhanced Conversions: Optimizing Core Web Vitals can lead to higher conversion rates. Users are more inclined to complete desired actions—such as making a purchase or filling out a form—when their experience is smooth and enjoyable.
- Long-Term Sustainability: As web technologies and user expectations evolve, maintaining a focus on Core Web Vitals positions your site for long-term success. Regularly optimizing these metrics helps future-proof your website against changing search algorithms and user behaviors.
Key Takeaways and Next Steps for Website Optimization
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously assess your Core Web Vitals using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Google Search Console, and Lighthouse. This helps identify performance issues and track improvements over time.
- Implement Best Practices: Focus on technical optimizations, such as image compression, lazy loading, minimizing JavaScript, and improving server response times. Ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is also crucial, as many users access sites via mobile devices.
- Prioritize User Experience: Take a user-centric approach to design and content delivery. Make sure that your website provides a smooth, engaging experience to keep users coming back.
- Seek Expert Help: If you encounter challenges in optimizing Core Web Vitals, consider engaging with specialists or agencies that offer Core Web Vitals optimization services. They can provide targeted strategies and insights tailored to your website’s needs.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of Google’s evolving algorithms and user experience guidelines. Regularly updating your website’s performance practices ensures you remain competitive in search rankings.
Optimizing Core Web Vitals is not just about improving performance metrics; it’s about enhancing user experience and fostering growth. By prioritizing these metrics, you can significantly boost your website’s SEO success, attract more visitors, and ultimately drive conversions. Make Core Web Vitals a key focus of your website optimization strategy, and take actionable steps to ensure your site meets the expectations of users and search engines alike.
